

Percentage dehydration × body weight (kg) × 1000 × 0.80 g.

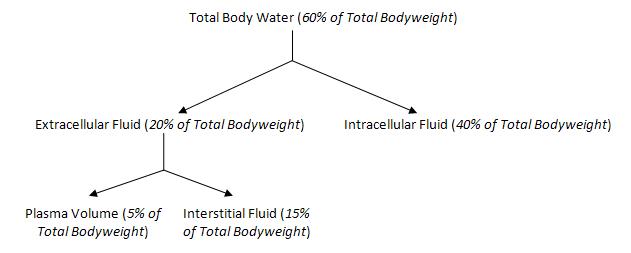
can calculate the volumes of the intracellular and extracellular compartments. Fluid deficits can be calculated by using the following formulas 5 (1 lb of water 454 mL 1 kg of water 1000 mL): Percentage dehydration × body weight (lb) × 454 × 0.80 g. These differences are greatest in premature babies, when ECF exceeds ICF. To evaluate TBW, ECW and ICW by the fluid volume model, the BCM defines extracellular and total body resistance by the. Example: tritiated isotope of water 3H2O is injected into a 90 kg woman to determine her total body water. All molecules and ions in the body fluids, including water molecules and. The ICF volume is obtained by subtracting the ECF volume from the TBW.ĮCF exceeds 30% and ICF is <40%. The interstitial fluid volume is determined as the difference between ECF volume and plasma volume. NaCl fluid from body, calculate amount of ECF loss in all three conditions. Approximately 67 of total body water (or 40 of total body weight) is in the intracellular fluid (ICF) compartment, which is the fluid that is present in the cytoplasm of all cells of the body. This compartment includes fluid in the synovial, peritoneal, pericardial. If we use 70 kg (155 lb) to represent the average adult male, the total volume of water in the body can be calculated to be about 42 L. In a typical adult male human, approximately 60 of the total body weight is composed of water. These substances neither leave the vascular system nor penetrate the erythrocytes. Body fluid compartments of a 70-kg adult man. Plasma volume can be measured either by radioactive albumin or by Evans blue. Recognize the clinical signs and symptoms associated with disorders of extracellular fluid. ECF volume is measured using inulin, which is proportionally distributed between plasma volume and interstitial volume. Calculate human body fluid compartments for a given body weight. TBW is measured using deuterium oxide (heavy water). Vol1 = volume of indicator, Vol2 = volume to be measured.Īgents used for measurement of fluid compartments Thus, the intracellular fluid constitutes about 40 percent of the total body weight in an average person. INTRACELLULAR FLUID COMPARTMENT About 28 of the 42 liters of fluid in the body are inside the 100 trillion cells and are collectively called the intra-cellular fluid. Relationship between the volumes of major fluid compartmentsĪ known amount of tracer is introduced into the space to be measured, and its concentration measured after mixing.Ĭon1 = initial concentration of indicator, Con2 = final concentration of indicator accordingly when considering body fluid compartments in most people. 3, 4, 5 Note that 1 kg is equivalent to 2.2 lb, 1 inch is equivalent to 2.54 cm, and 1 L of water weighs 1 kg (2.2 lb).Total body water (TBW) constitutes 55-60% of the body weight in men and 45-50% of the body weight in young women. × ) and females’ lean body weight = 45.5 kg + (2.3 kg/in. In healthy lean people, the total body water comprises 50-60 of body weight in men and 45-50 of body weight in women.1 These differences in total body water percentage between men and women are because of women typically having less muscle mass and a greater amount of adipose tissue than men. 2 In obese patients, it is customary to estimate TBW using lean body weight or IBW as calculated by the Devine–Devine method: males’ lean body weight = 50 kg + (2.3 kg/in. Unless the patient is obese (body weight greater than 120% of ideal body weight ), clinicians typically use a patient’s actual body weight when calculating TBW. ECF is divided among two subcompartments: plasma and interstitial fluid. The percentage of TBW decreases as body fat increases and/or with age (75%–85% of body weight is water for newborns). BODY FLUIDS one third of total body water or 20 of body weight. For clinical purposes, most clinicians generalize that total body water accounts for 60% of lean body weight in adults, regardless of gender. KEY CONCEPT TBW constitutes approximately 50% of lean body weight in healthy females and 60% of lean body weight in males. Calculation of Plasma Volume, Blood Volume and Red Cell Volume. The most fundamental concept to grasp is an assessment of total body water (TBW), which is directly related to body weight. are important in physiological studies of body electrolyte and fluid homeostasis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
